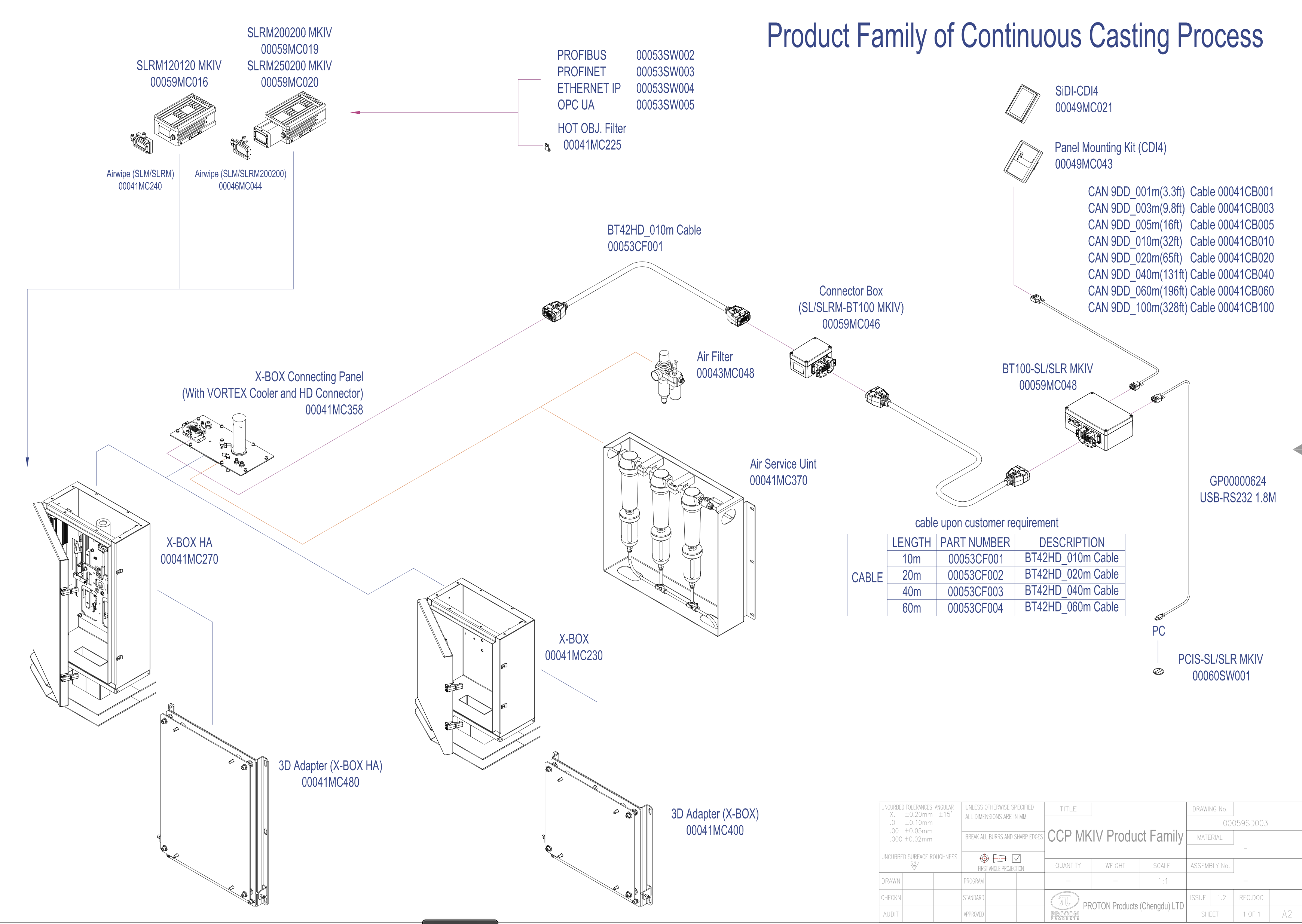
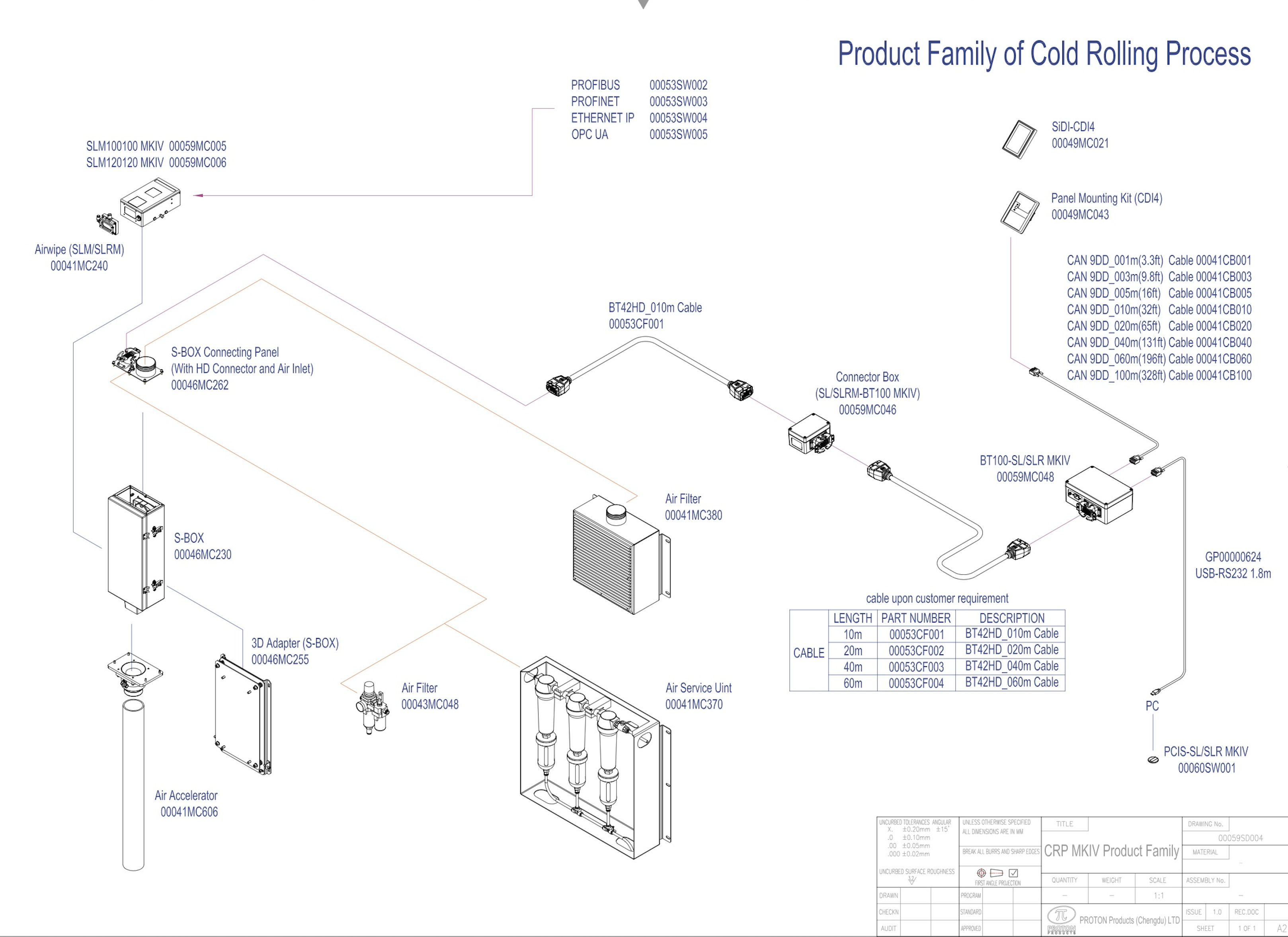
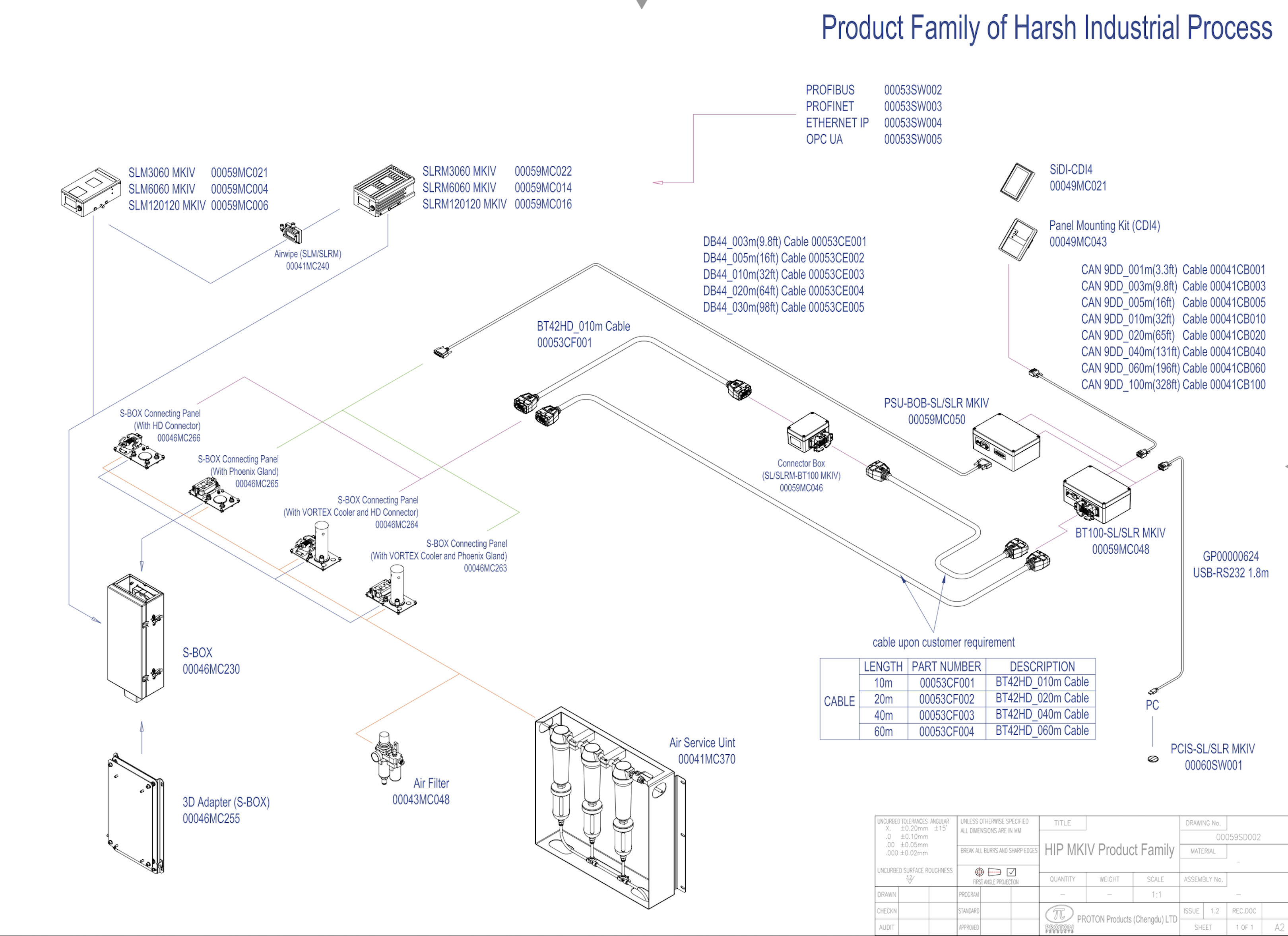
Introduction
The manufacturing industry has witnessed a significant transformation over the years, driven by technological advancements. Industry 4.0, often referred to as the Fourth Industrial Revolution, has played a pivotal role in reshaping traditional manufacturing processes across various sectors. In this blog, we will explore the applications of Industry 4.0 in the manufacturing of steel wire and cable, shedding light on how this revolution is enhancing efficiency, quality, and sustainability in the industry.
Industry 4.0 Essentials
Before delving into the specifics of steel wire and cable manufacturing, let’s briefly understand the core principles of Industry 4.0:
- Interconnectivity: Machines, devices, and systems are connected through the Internet of Things (IoT), enabling seamless communication and data exchange.
- Data Analytics: Big data and analytics are used to collect, analyze, and interpret vast amounts of data, providing valuable insights for decision-making.
- Automation: Automation technologies, including robotics and autonomous systems, are employed to optimize processes and reduce human intervention.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): AR and VR are used for training, maintenance, and design, enhancing the overall manufacturing experience.
- Cybersecurity: Protecting data and systems from cyber threats is crucial in an interconnected environment.
Applications in Steel Wire and Cable Manufacturing
- Predictive Maintenance:
- Industry 4.0 allows manufacturers to implement predictive maintenance strategies. Sensors placed on machines and equipment collect real-time data, such as temperature, pressure, and vibration, to predict when maintenance is needed. This prevents unexpected downtime and reduces maintenance costs.
- Quality Control:
- High-quality steel wire and cable are essential for safety and performance. With Industry 4.0, automated inspection systems use cameras and sensors to detect defects and ensure product consistency. Machine learning algorithms can even learn from historical data to improve inspection accuracy over time.
- Inventory Management:
- Smart inventory management systems with RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) technology enable manufacturers to monitor raw materials and finished products in real-time. This helps in optimizing stock levels, reducing waste, and ensuring timely production.
- Energy Efficiency:
- Steel wire and cable manufacturing can be energy-intensive. Industry 4.0 solutions optimize energy usage through real-time monitoring and control of equipment. This not only reduces costs but also contributes to sustainability efforts.
- Supply Chain Optimization:
- Manufacturers can leverage data analytics to optimize their supply chains. Predictive analytics can forecast demand, helping in procurement and scheduling production accordingly. Additionally, blockchain technology can enhance transparency and traceability throughout the supply chain.
- Customization and Flexibility:
- Industry 4.0 enables mass customization in manufacturing. Smart factories can quickly adapt to changing customer demands and produce tailored steel wire and cable products efficiently.
- Worker Safety:
- Augmented Reality (AR) is used for worker training and safety. AR glasses can provide real-time instructions, helping workers perform tasks accurately and safely. Furthermore, robots can handle dangerous tasks, reducing the risk of accidents.
- Data-Driven Decision Making:
- The abundance of data generated in smart factories allows for data-driven decision-making. Manufacturers can analyze production data to identify bottlenecks, optimize processes, and improve overall efficiency.
Challenges and Considerations
While Industry 4.0 offers numerous benefits to steel wire and cable manufacturing, there are some challenges and considerations to keep in mind:
- Initial Investment: Implementing Industry 4.0 technologies requires a significant initial investment in infrastructure, sensors, software, and training.
- Cybersecurity: As connectivity increases, the risk of cyberattacks also grows. Manufacturers must prioritize cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive data and systems.
- Workforce Skills: Employees need training to adapt to the new technologies and processes. Upskilling the workforce is essential for a successful transition.
- Integration: Integrating existing systems with Industry 4.0 technologies can be complex. Compatibility and seamless integration are crucial for maximizing benefits.
Conclusion
The application of Industry 4.0 in the manufacturing of steel wire and cable represents a transformative journey toward greater efficiency, quality, and sustainability. Predictive maintenance, quality control, energy efficiency, and data-driven decision-making are just a few examples of how Industry 4.0 is revolutionizing this industry. As technology continues to evolve, manufacturers who embrace these advancements will be better positioned to thrive in a competitive global market while contributing to a more sustainable future.